Flexible Humidity Sensor Based on Electrochemically Polymerized Polypyrrole
Qi Zhao, Xiang Qian, Xiaohao Wang, Liwei Lin
Xiang Qian* (Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University) qian.xiang@sz.tsinghua.edu.cn
Environmental sensing is an important task in the development of infrastructures for the applications of the Internet of things. In this work, we introduce a flexible humidity sensor based on electrochemically polymerized polypyrrole to absorb or desorb water vapors to detect relative humidity (RH). A test platform was built to mix the different amounts of dry and wet air for the relative humidity ranging from 15% to 95%. Experimental results show that the response time from 20% to 90% RH of the sensor was 505 seconds and the recovery time from 90% to 20% RH was 328 seconds with good repeatability during three cycles. The wide dynamic range, excellent repeatability and reasonable response time make the sensor applicable for home monitoring applications. Furthermore, the flexible sensor is suitable for embedding into wallpaper or decorations for promising future systems to map the environmental status of buildings and homes.
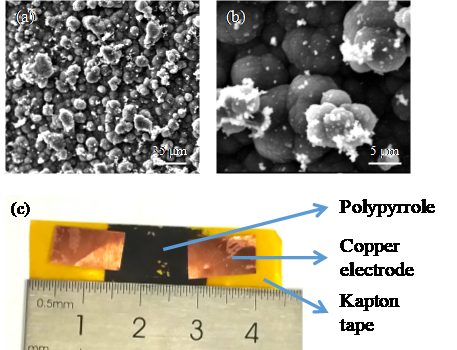
Fig. 1. (a) (b) Scanning electron microscope image of polypyrrole. (c) The finished sensor.

Fig. 2. Schematic of the humidity test platform.
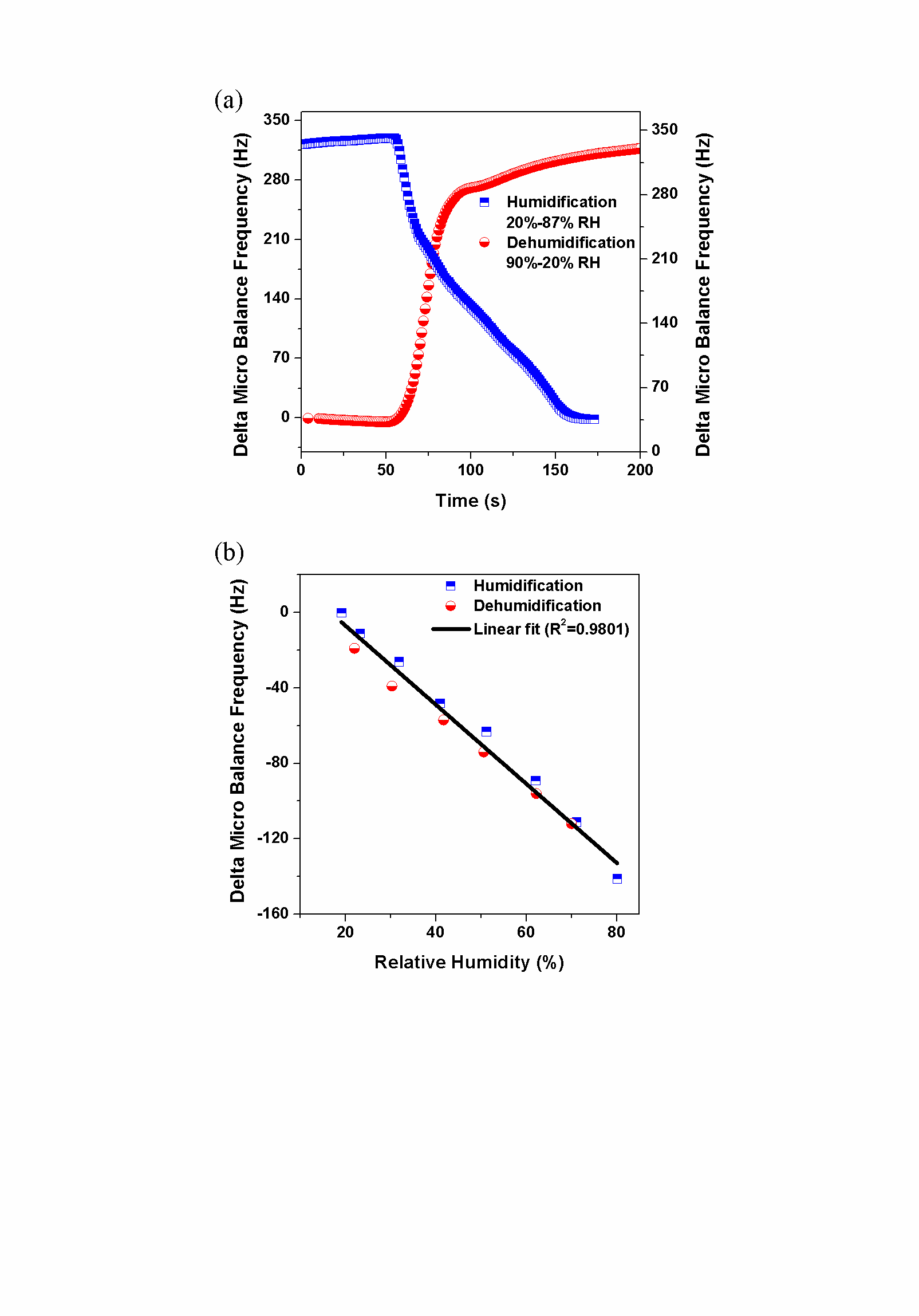
Fig. 3. Test results of polypyrrole material. (a) Humidification and dehumidification test. (b) Relationship between relative humidity and delta micro balance frequency.
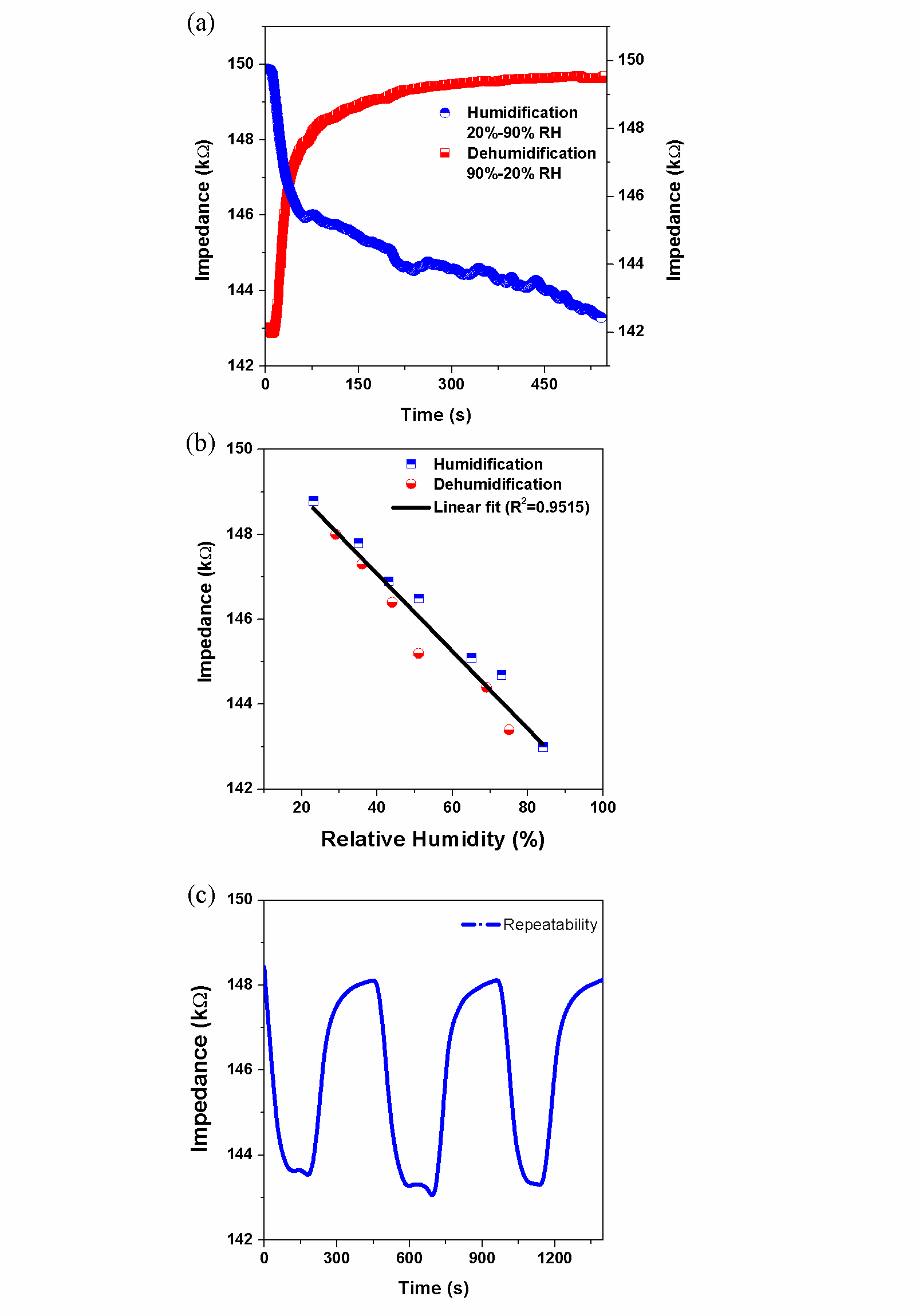
Fig. 4. Test results of the fabricated sensor. (a) Humidification and dehumidification test. (b) Relationship between relative humidity and the impedance of the sensor. (c) Impedance change during the three measures cycles (20%-80% RH).